Contents
Related Help Documents
Description
Genelists are text files which specify a set
of "genes". They can be used to customize data retrieval, normalization
and other tasks. "Genes" can be identified by name, suid, and
other identifiers.
Only registered users of the database may use genelists, since the
files are stored locally in your loader account, in the
"genelists" directory. They are accessible via
sFTP, and may be downloaded,
created or edited on your desktop machine, and uploaded as
desired.
Genelists may be used for data retrieval. Groups of "genes" may
be combined into a genelist and selected as a group in
Advanced Results Search for
retrieving a subset of the full data. Genelists may also be used to
normalize data,
Calculate Q-score
and collapse data using
Synthetic genes.
There are several applications that use genelists specific for the
application. These specialized genelists are available for all
database users. Specialized genelists are available during data
retrieval as part of the gene selection process, for the
Synthetic Gene tool and for
Q-score calculation.
Creating a
genelist on your desktop computer
Genelists are tab-delimited text files, which may be easily created in
a spreadsheet program like Excel. See
below for the format. It may also be
convenient to download an already-created genelist, and edit it to add
or remove genes or annotation. Examples for genelists can be
downloaded from here: using
cloneids or
goids.
When finished, save the list as a tab-delimited text file, and
upload it to your loader "genelists" directory using
sFTP.
Genelist format
Genelists are tab-delimited text files. The order of the
columns is arbitrary and only the column headers specified in the
table below are understood
Allowed Column Headers
|
Requirements
|
Description
|
NAME, SUID, LUID, SPOT, GOID or
GOTERM
|
One and only one must be included.
|
Identifies the type of gene
identifier.
- NAME: can mean either CLONEID or ORFNAME
(E.g.: IMAGE:1542757; YLR326W; HPY1808)
- SUID: Sequence unique identifier - unique for a
sequence
- LUID: Laboratory unique identifier for an instance of a
sequence
- SPOT: The spot/feature within a
print design
- GOID: Gene Ontology id to which a gene was
annotated (e.g.: GO:0006616)
- GOTERM: Exact name of the Gene Ontology term to which a gene was
annotated (e.g.: 'nuclear envelope')
|
ANNOTATION
|
Optional column
|
Annotation for the 'gene' that
you would like to include in your analysis in place of database-derived annotation.
|
WEIGHT
|
Required for synthetic gene application.
|
Weight for the gene in
calculating the synthtic gene value. It should be a value between 0 and 1.
|
CHILDREN
|
Optional, used when the
identifier used is GOID or GOTERM.
|
0, or missing value indicates
that only genes that are directly annotated to the GOID/GOTERM are
to be retrieved. Any other value will retrieve genes that are
annotated either directly to the GOID/GOTERM or to its children.
|
Using Genelists
Data Retrieval: Data from the database will be retrieved
for only the "genes" that are listed in your genelist file. You
can select the genelist on the "Gene Selection and Annotation"
page of data retrieval. First, you need to indicate you would like
to use a genelist from your loader account by selecting the radio
button, then select a genelist from the pulldown menu. (See
Figure
1.). If you have annotation in the genelist file that you would
like to keep during the rest of your analysis, you can do this on
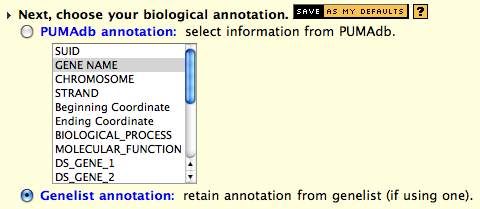
the same page. Select "Genelist Annotation" under the biological
annotation section (see
Figure 2.).

|
|
Figure 1: Data Retrieval by Genelists.
|
|
|
Figure 2: Keep biological annotation from Genelists.
|
Q-Score: Q-Score calculations for arrays will be performed
using only the "genes" that are listed in a selected genelist. For
further help, please look at the
help document for Q-Score.
Normalization by Genelist: Using this application you can
calculate a normalization value for an array using only the
"genes" listed in a selected genelist. For further help, please
look at the related
help
document.
Synthetic Genes: For further help, please
look at the related
help
document.

